Keywords
|
| M-Banking; M-commerce; E-commerce; ICT, and 3G (Third Generation network) |
INTRODUCTION
|
| The telecommunication Industry has witnessed considerable advances in the last one decade. The major changes has come in the delivery of the content, applications and services to the mobile and other wireless communication devices. M-Commerce is an emerging area which refers to Mobile Commerce and defined as the use of a wireless terminal like a cellular telephone, smart phone or Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) and a network to access information and conduct transactions that result in the transfer of value in exchange for information, goods and services and is likely to put at test the regulatory mechanism that are in place to deal with the traditional transactions.United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) defined M-Commerce as buying and selling of goods and services using wireless hand-held devices. M-Banking is equally referred to as mobile e-Banking. It is defined as the newest channel in electronic banking that provides a convenient way of performing banking transactions, which is also known as “pocket-banking” (Charles, 2006). |
| M-Commerce refers to the different types of business transactions that are conducted on mobile devices using wireless networks. M-banking is also equally refereed as mobile Ebanking. It is considered to be the latest gateway in electronic banking that provides a platform for doing banking transactions presenting M-banking as the medium of providing financial services using mobile telecommunication devices. |
| The major difference between the electronic and mobile business transaction highlighted by the prefixes “e” and “m” is that the electronic medium offers “anytime access”, while mobile offers “anytime and anywhere access” for business transactions (Tiwari et al.,2006). The other major differentiating factor is that electronic transactions are limited to computer networks that are fixed in nature, while mobile transactions refers to computer networks that support both stationary and wireless connectivity. M-Commerce feature can be highlighted as absolute, immediacy, real-time, localization, proactive functionality (through SMS), and simple making sure procedure (based on a subscriber identification module (SIM) and personal identification number (PIN) (Tiwari et al.,2006). |
Mobile Services in Oman
|
| Mobile commerce is one of the promising areas that involve mobile devices, wireless networks and Internet technologies. The Sultanate of Oman has also experienced a phenomenal growth of the telecommunication industry and it is among one of the fastest in the Arab world. The Omani telecommunication industry is dominated by two major companies- Oman Mobile and Nawras, but in the last one year three more companies have entered in the market i.e. Mazoon, Friendi, and Renna. All these companies are offering 3G+ services which offer the high speed broadband internet services, wide area wireless voice telephony and data transfer services. This trend has immensely helped some of the major sectors of the economy like telecommunications, banking and ecommerce specially. |
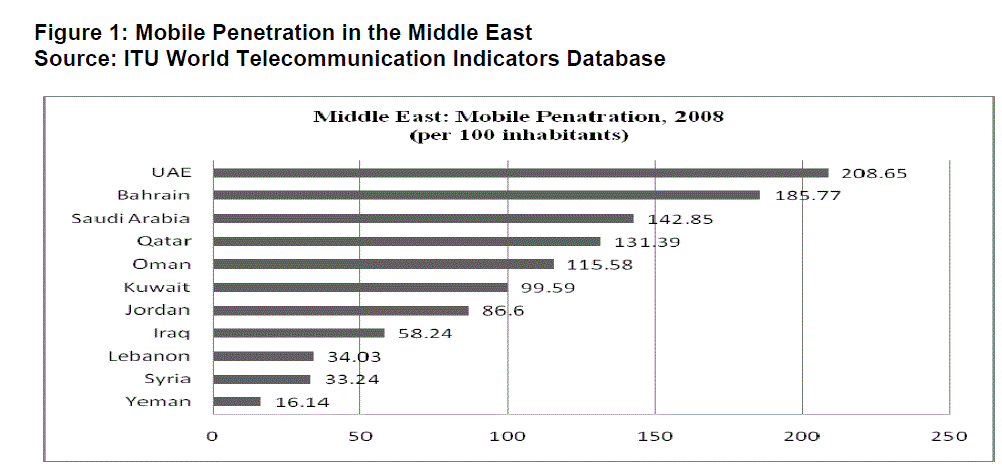
| According to ITU (2009), the Sultanate of Oman had 3.2 million mobile subscribers in 2008 with a growth rate of 40.2%. Mobile penetration in Oman is approximately 115.58% which has witnessed a high degree of mobile penetration in the past few years (see Figure 1). In the time span of 5 years marked between Year 2003 and Year 2008, number of mobile subscribers has increased more than 5 times reaching 3.2 million. However, fixed line subscribers grew only by 38,000 during that period (Figure 2). |
| These major developments in the field of telecommunications technology has helped the growth of M-Commerce technology where business can be conducted electronically anytime anywhere. Riding on the success of the E-Commerce, Mobile commerce is considered to be the next technological evolution because of the rapidly changing needs of the customers. Customers are more demanding now a days, keeping in view their lifestyles, they need faster and more reliable wireless technology. M-Commerce is the right solutions for this demand as it makes traditional E-Commerce task to be performed easily through cell phone or PDA’s over wireless networks. |
Mobile Operators in the Sultanate of Oman
|
| Oman Mobile is the leading telecom service provider with market share of 60% (See omantel.com). The basis for this is that it has the maximum network coverage, several schemes which gives the customers value for money and a range of wireless and data services to the users of the network having an advanced 3G+ network. The other leading service provider Nawras has also giving a tough fight and has also introduced 3G+ platform for its consumers which is supposed to boost the M-Commerce operations in the Sultanate. Currently almost all the banks are providing some form of E-banking and M-Banking such as Internet access, account information and funds transfer etc. |
LITERATURE REVIEW
|
| Mobile commerce is considered to be an extension of E-Commerce that provides user to interact with other users or businesses using the wireless platform as anytime & anywhere accesses. The vibrant Omani market, with high level of technological acceptance provides an encouraging environment for M-Commerce growth. However, there has been no significant research done in this field in the sultanate of Oman. |
| Charles et al., (2007) conducted a study on the M-commerce in the banking sector of Nigeria. The paper deals with the issue of adoption of ICT in the banking sector using SWOT analysis. It was found out that all banks in Nigeria offer e-banking and around 52% of them also offer some form of M-banking services. The potential is great for MCommerce but due to lack of infrastructure support the implementation is not smooth. |
| Coursaris & Khaled (2003) studied M-Commerce in Canada focusing on the issue of wireless privacy. An analysis of the Canadian Mobile market has been done with respect to both E-Commerce and M-Commerce followed by discussion of the needs and concerns of Mobile customers. The study is focusing on the privacy concern which arises because of the wireless interaction between the two parties and presents a framework for this. Also the responsibilities of the interacting parties for increasing the privacy have been highlighted. |
| Tiwari, Buse, and Herstatt (2007), in their study titled, “Mobile Services in Banking Sector: The Role of Innovative Business in Generating Competitive Advantages" have empirically assessed the customer acceptance of the M-Commerce in Germany. The study found that the highest users of mobiles are the top management of the corporate, self employed, salaried persons, students and others. It was found that Government employees were found not supporting mobile banking. Some of the reasons that came in favor of mobile banking is its ubiquity, overview of bank account and immediacy. However the concerns of the users were mainly regarding the insecurity and high cost. |
E-Banking and M-Banking Services in Oman
|
| Table 2 gives an account of the present status of e-banking services in the sultanate. It is found that almost all banks more or less are providing banking services using ICT platform for efficient and effective delivery of services. |
Application of Mobile Commerce
|
| The commercial business transactions, which till now were being offered only on electronic medium, are now being offered on the fast emerging mobile platform. This has been due to the exponential rise in the number of mobile devices all over the world with one-third of the world population having access to it has boosted M-Commerce (Tiwari, 2006b). |
| Some of the mobile applications are presented by Tiwari are modified and compiled in table 3 which is as follows |
METHODOLOGY
|
| The paper is an attempt to assess the level of Information and Communication Technology adoption by the banking industry and to assess the prospects and user perceptions of M-Banking in the Sultanate of Oman. Two hundred fifty (250) questionnaires were administered to businessmen, banks academics and students out of which one hundred and ninety six (196) were returned. The data collected using questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS software. |
| In this study two research tools were put to use. The first one is the exploratory review of secondary data obtained through internet and other secondary sources available such as report from the concerned banks and telecom services providers as well as information available on their websites. The second one was survey questionnaire that were distributed to access user perceptions of Mobile banking in the Sultanate of Oman. |
DATA FINDINGS AND ANALYSIS
|
| Table 4 gives an account of the demographic profile of the respondents on the basis of their gender, age and educational status. |
| From the table it can be observed that the total respondent were 196 in number out of which 42(21.4%) were male and 154(78.6%) were female. This indicates that the female are more active in all the organizations in Oman. The age group analysis shows that the majority of the respondents are in the age group of 18-30 years which accounts for whopping 91.8%. The respondent in the age groups of 31-40, 41-50 and 50 above years were only few and stood at 4.1%, 2% and 2% respectively. This shows that the users of the modern gadgets are young. The analysis of the educational status tells that majority of the respondent were Diploma holders which was 46.9%, followed by High school 26.5%, Higher degree 21.4% and degree holder only 5.1 percent. It can be deduced from this that major chunk of the respondents were well educated and the total Diploma, Degree and Higher Degree constituted for 73.4% of the total. |
| Currently there are two the types M-Commerce services provided by the banks in Oman such as M-Banking and SMS Banking. From the analysis of table 5, it came out that 41.8% of the responders acknowledged that they use their mobile for banking services while 58.2% are not using theses service. It also shows that responses regarding the awareness of the respondents about the availability of types of mobile banking services, 49% respondents were aware about the SMS banking services while 15.3% think that mobile services are available and 35.7% are not sure about any kind of mobile services available in Oman. Table 5 list the advantages of M-banking such as ubiquitous 43.9%, fast reaction in market development 55.1%, paying bills 42.9% and viewing the account statements 26.5%. |
| Table-6, asses the number of respondents having a mobile or not and 96.9% own a mobile phone while only 3.1% do not have mobile phones. This shows that the mobile users are huge in numbers. The table also gives an account of the types of phones used by the respondents. 46.9% use cell phones, 49% use smart phones and rest use 4.1% use Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs). It is indicating that only 50% respondents access the web using their mobiles showing that some of them have WAP facility embedded in their devices. |
| Table 7 shows the respondents perception of threats of using M-Banking, which include security of transactions and unavailability of basic infrastructure. Security threat was the major concern of the respondents which stood at 60.2%, while 16.3% considered it as complicated to use and 44.9% felt it to be costly to use. It was also noted during the study that cost of the mobile services is very high in Sultanate of Oman as compared to other developing countries of the world. |
CONCLUSION
|
| All the banks in Oman use the ICT for prompt delivery of banking services like credit cards for e-payments, internet banking and mobile banking services. But M-Banking activities are limited to mobile finances information like Balance Enquiry, Mini Statement, Cheque Book request, Request to stop all ATM Cards, Exchange rates (Indicative rates), Credit Card Balance Enquiry, Salary Credit, ATM Withdrawal, Point of Sale (POS) Transaction, Fixed Deposit Renewal, Loan Overdue, Cheque bounced, Speed Transfer Transaction - Accepted / Rejected, Customer deliverables acceptance acknowledgement (Debit Card and Pin, Credit Card and Pin, Internet Banking Pin, Call Center Pin, Cheque Book). |
| The banks and telecom companies are well equipped to offer quality electronic and mobile services. Presently most of the banks are offering some form of M-banking but the services are very few. Although most of the banks are working on to provide other Mbanking services on priority basis. However, some coordinated approach has to be adopted by the financial services providers and telecommunication companies, so that M-banking services can be implemented. The 3G network which is already in place will definitely provide support in increasing M-Commerce activities in Oman. It will further boost with the availability of advanced mobile devices which provide a platform for easy and secure wireless financial transactions. |
| M-Commerce has numerous opportunities for expansion in Oman keeping in view the development of the institutions which are responsible for its growth. However, at the same time the threat perception such as security of transactions, complexity of operations and high cost of services which is major issue highlighted by the users also needed to be addressed to put the users of M-Commerce at ease. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
Table 3 |
Table 4 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 5 |
Table 6 |
Table 7 |
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
|
| |
References
|
- Ayo Charles, K. (2006) The Prospects of e-Commerce Implementation in Nigeria, Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, Vol. 11, No.3 (http://www.arraydev.com/commerce/jibc/)
- Charles K. Ayo, Uyinomen O. Ekong and Ibukun T. Fatudimu (2007), "The Prospects of m-Commerce Implementation: Issues and Trends, in Information Management in in the Networked Economy: Issues & Solutions", Proceedings of the 8th IBIMA Conference, Ireland, , pp210-216
- Coursaris, C., Hassanein, K., and Head, M. (2003), “M-Commerce in Canada: An Interaction Framework for Wireless Privacy”, Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences, 20(1), 54-73.
- Tiwari R. et al. (2007) Mobile Banking as Business Strategy: Impact of Mobile Technologies on Customer Behaviour and its Implications for Banks. Working Paper, Germany. Retrieved Feb. 2007
- Tiwari, R. S. Buse, and C. Herstatt. (2007), Mobile Services in Banking Sector: The Role on Innovative Business in Generating Competitive Advantages, in Proceedings of the International Research Conference on Quality, Innovation and Knowledge management, New Delhi, pp 886-894
- Tiwari R Buse S. (2007), The Mobile Commerce Prospects: A Strategic Analysis of Opportunities in the Banking Sector, Hamburg University Press, Germany
- UNCTAD (2004), E-Commerce and Development Report 2004, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, New York.
|