ISSN: 1204-5357
ISSN: 1204-5357
| AHMAD KABIR USMAN, MSc Researcher, Lancashire Business School, University of Central Lancashire, UK Postal Address: Lancashire Business School, University of Central Lancashire, Greenbank Building, Preston, Lancashire, PR1 2HE Email: ausman2@uclan.ac.uk Ahmad Usman is a research student at the University of Central Lancashire. His areas of interest are E-Banking Security and Biometric Technologies. MAHMOOD HUSSAIN SHAH, PhD Senior Lecturer, Lancashire Business School, University of Central Lancashire, UK Postal Address: Lancashire Business School, University of Central Lancashire, Greenbank Building, Preston, Lancashire, PR1 2HE Email: mhshah@uclan.ac.uk Dr. Mahmood Shah is a Senior Lecturer in Business Systems and Cyber Security at the University of Central Lancashire. His research interests are in the areas of cyber security, e-banking, identity theft prevention in e-retailing, e-business and Information Systems. |
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce
E-Banking fraud is an issue being experienced globally and is continuing to prove costly to both banks and customers. Frauds in e-banking services occur as a result of various compromises in security ranging from weak authentication systems to insufficient internal controls. Lack of research in this area is problematic for practitioners so there is need to conduct research to help improve security and prevent stakeholders from losing confidence in the system. The purpose of this paper is to understand factors that could be critical in strengthening fraud prevention systems in electronic banking. The paper reviews relevant literatures to help identify potential critical success factors of frauds prevention in e-banking. Our findings show that beyond technology, there are other factors that need to be considered such as internal controls, customer education and staff education etc. These findings will help assist banks and regulators with information on specific areas that should be addressed to build on their existing fraud prevention systems.
Keywords |
| E-Banking; E-banking Frauds Prevention; Internet Banking Security; Fraud Prevention; Critical Success Factors |
INTRODUCTION |
| Electronic banking services are the banking class of services that can be offered by a bank to individuals and companies through electronic means via a fixed or mobile telephone, and Internet (RATIU, 2011). Given that internet technology has evolved considerably over the years, newly developed e-banking services now differ considerably from older systems (Khan and Mahapatra, 2009). Some of the more common types of E-Banking services today are Online Banking, Automated Teller Machines (ATM), Electronic Funds Transfer, Electronic Cheque Conversion, Direct Payment and Web ATM services. There are many security issues related to all of these services and this paper aims to highlight factors that could be critical to the prevention of fraud in the e-banking space by reviewing relevant literature. |
| The online banking channel is the cheapest delivery channel for delivering banking products once established (Sathye, 1999 and (Tero Pikkarainen, 2004). Therefore it is no surprise that the banks globally are continuing to shift towards e-banking services. With the growing patronage of e-banking services and its anticipated dominance in the near future, some of the known factors that contribute to addressing the acute problem of security must be addressed. This paper identifies and synthesises a number of that factors such as the availability of funds, change management, timely access to information and strict internal controls could all prove vital for reducing e-banking fraud. Exposure to such factors provides regulators and bank management teams an insight into areas that may require increased emphasis and improvement. |
Systematic Literature Review |
| The research makes use of a systematic literature review taking into consideration ebanking fraud and other electronic fraud or security related literature. A systematic literature review ‘‘is a means of identifying, evaluating and interpreting all available research relevant to a particular research question, or topic area, or phenomenon of interest’’ (Kitchenham, 2007). Therefore ensuring thorough coverage of pertinent literature using a systematic approach. This was done using an iterative search strategy as the review evolved rather than predetermined linear search strategies as recommended by (Finfgeld-Connett, 2013). |
| The literature review was carried out in 3 phases inline with the guidelines of (Kitchenham, 2007). |
| These are: |
| 1. Planning the review. This includes identifying the need for a review, specifying the research question and then developing & evaluating the review protocol |
| 2. Conducting the review. This phase involves identification of the research, selection of the primary studies, study quality assessment, data extraction and synthesis. |
| 3. Reporting the review. This is where the dissemination mechanisms are specified and then formatting and evaluation of the main report. |
| In order to perform searches for relevant literature, a selection of data sources was made. The databases that were used are: |
| • Academic Search Complete |
| • E-Journals |
| • Web of Knowledge |
| A number of keywords were used for searching databases to find relevant literature for the review. They are given below: |
| • Fraud Prevention Critical Success Factors |
| • E-Banking Fraud Prevention Technology/Security/Measures/Software |
| • E-Banking Fraud |
| • Fraud Prevention |
| • E-Banking Security |
| While searching, advanced search features such as applying related words and searching within the full text of articles were utilised. After each search had been completed, the results were reviewed and the most relevant literature was selected for use. |
E-BANKING SECURITY CHALLENGES |
| The introduction of E-Banking has come with its challenges. These range from technology adoption, financial limitations, and technology acceptance of new systems. Other factors experienced globally are the increase in security fears, cultural barriers, limited internet access and legislation (Masocha, 2010). Auta (2010) found that security, user friendly, queue management, accessibility, time factor and fund transfer are major factors in the adoption of e-banking and that security is rated as the most important issue of online banking services. Research conducted by Agboola and Salawu (2008) is in agreement with this. Security concerns are of greatest importance for the adoption of e-banking services (Angelakopoulos, 2011 4). Hence, the desire to understand these challenges in more detail and adopt initiatives to address them. |
| Security is a factor that is constantly highlighted as a CSF for the success of E-Banking. The inadequacy of security potentially leads to financial losses, punitive measures by regulators and negative media publicity (Shah et al, 2012) therefore its importance cannot be over emphasised. In E-banking, fraud is a major contributory factor to the term security and needs to me managed closely. ‘‘Incentives for fraud increase when transactions are made in large amounts, when transactions are made anonymously or at the point of sale, when claims cannot be effectively verified at the point of sale, and when issuers of payment claims bear the costs of fraudulent transactions’’ (Roberds 1998). E-Banking offers most if not all these incentives, hence the need for adequate fraud prevention strategies. |
| In 2010, most of the fraud cases were perpetuated via electronic banking systems therefore reflecting weaknesses in the internal control systems (CBN Annual Report, 2010). Financial services and organisations suffer yearly losses through crimes such as online banking, cheque and card fraud (Adams, 2010). These clearly indicate that criminals are exploiting e-banking mediums. Hence the need for improved continuous improvement in security to prevent fraud (Giles, 2010) and mitigate the risk of customers’ losing confidence in e-banking services. More recently, there has been some improvement in preventing fraud over electronic banking mediums. Financial Fraud Action, 2011 reported that in the UK, Fraud losses on credit/debit cards were at a 10 year low while online banking fraud losses fell by 24%. This has been attributed to improved e-banking security through both technological and non-technological approaches. Research aimed at minimizing fraud has proved popular extending beyond the banking industry to online auctions (Cecil Eng et al. 2007;Chang and Chang 2011), healthcare (May 2010), Insurance (Ormerod et al. 2012) to fraud prevention in the telecommunications industry (Estavez et al. 2006) where 56.2% of fraudsters were able to be identified by testing a fraud prediction module. However, research into factors critical to e-banking fraud prevention is limited. |
E-Banking Fraud |
| Although there is no single accepted definition of fraud (The Legal Practitioner, 2013), it relates to wrongful or criminal deception that results in financial or personal gains. Bank Fraud is the use of deliberate misrepresentation (which usually requires some technical expertise) in order to fraudulently obtain money or other assets from a bank (wiseGeek, 2013). The types of fraud that are commonly experienced by financial institution include sales fraud, purchase fraud, cheque payment fraud and ATM fraud (Benjamin, 2011). Other strategies employed include collaborating with security agents and bank officials as well as local and international networking (Aransiola, 2011). Worryingly, results show that internal personnel of banks had been collaborating with fraudsters. This presents a real threat as internal personnel have direct access to banking systems and access to customers’ personal information and records. According to the FBI, the majority of fraud is committed by employees who exploit breakdowns in organisations (Sidden, 2005). Research to understand why internal staff opts to engage in such activities exists. (Benjamin, 2011) found that perceived inequality and perceived job insecurity had significant effect on employee fraudulent intent. Such findings help highlight that beyond technology, there are other factors capable of impacting fraud that come into play. |
| Phishing is one of the mechanisms that fraudsters use to obtain customers personal details leading to its use for fraudulent activities. Amtul (2011) states that such challenges presented by phishing results in companies loosing thousands of dollars, and emphasises the need for biometrics to help checkmate such activities. In addition, statistics show that 35.9% of the financial sector is the target for phishing. A Javelin Identity Theft Report (2010) stated that there was a 12% and 12.5% increase in identity theft victims and fraud respectively. This not only highlights the fact that fraud and identity theft is on the rise, but that current security measures in place are insufficient. |
Critical Success Factors |
| Rockart (1979) defines CSFs as the limited number of areas in which results, if they are satisfactory, will ensure successful competitive performance for the organisation. CSFs are imperative in concept yet highly practical and as such readily understood and accepted by managers and practitioners (Butler and Fitzgerald, 1999). CSFs have been used for a variety of purposes ranging from manufacturing to IT System Implementations and are useful for planning and decision making purposes. |
| In contrast to this, Critical Failure Factors (CFFs) is a different approach that can be used to identify factors that tend to cause failure. Research shows that this approach is used less often and is suited to scenarios such as the work of Amid et al (2012) where frequent failures have occurred leading to the need âÃâ¬ÃËto identify such factors and classify them’ to help prevent failures in the future (Amid, 2012 11). However, Aziz and Salleh (2011) contradict this by arguing ‘‘identifying the critical success factors (CSFs) has become the main agenda for researchers, academicians and practitioners due to the wide number of failures reported’’. Therefore CSFs can still be applicable in such scenarios. |
Identifying CSFs |
| Both quantitative and qualitative research methods can be used to identify CSFs. Methods previously employed include literature reviews (Umble and Umble, 2001), case studies (Holland and Light, 1999), surveys and interviews interviews (Rockart and Van Bullen, 1986) just to name a few. Shah and Siddiqui (2006) concluded that the survey approach is the most commonly used method for the identification of CSFs. However, this does not imply that this is the most effective approach. This study used the systematic literature review methodology to synthesise existing relevant literature and identify factors that affect e-banking fraud globally spanning both the developed and developing nations. |
Critical Factors for Fraud Prevention |
| Bank stakeholders are constantly introducing new security measures with the aim of eradicating e-banking fraud, however existing measures have not been able to achieve this (Roberds 1998). Consequently, there is still need for research to narrow down on specific areas for improvement. Personally, I believe that improved authentication systems is the way forward and can play a significant role in e-banking fraud prevention. The common use of the same passwords for authentication increases the vulnerability whenever such information is stolen. Thus, an additional security measure is required to confirm the identity (Robert Moskovitch et al, 2009). Given that conventional methods of authentication via usernames and passwords are no longer sufficient (Vandommele, 2010), biometric technology has been identified as one of the potential technologies to improving security. |
 |
| Given the information above, two critical success factors can be derived from the review of existing fraud prevention measures. These are: |
| • Appropriate Technical Fraud Prevention Measures |
| • Innovative use of Fraud Prevention Technologies |
| The table above summarises some of the existing fraud prevention measures and shows how some of the more recent literature is shifting its attention to biometric technologies. Biometric authentication supports the facet of identification, authentication and nonrepudiation in information security (Bhattacharyya, 2009). Hence, this type of technology can potentially play a pivotal role in minimising e-banking fraud. Biometric technology is seen as a way forward due to every individual’s unique features that can be used for identification. Although advances in biometric technologies such as fingerprint and keystroke dynamics appear promising, (Murdoch, 2010) highlighted that secure authentication solutions need to be both technologically sound and economically viable. |
 |
| The table above highlights factors that researchers have placed emphasis on as a means of improving fraud prevention. Again, biometric authentication appears as a frontrunner and is covered in a number of papers. Research has proved that biometric technology can significantly decrease e-banking fraud and has already been implemented in some banks such as the biometric ATMs by First Bank in Nigeria. However instances of such deployments remain rare. Interestingly, Murdoch & Anderson, (2010) emphasised that authentication solutions need be both technological and economically viable. Therefore beyond looking at the accuracy of biometrics, their false rejection and acceptance rates, the cost of deploying such a technology comes into play. Fingerprint technology isn’t the only biometric technology available today with some banks opting to use Keystroke dynamics a behavioural biometric to improve their security. |
| âÃâ¬ÃËKeystroke Dynamics is the process of analyzing the way a users type at a terminal by monitoring the keyboard inputs thousands of times per second, and attempts to identify them based on habitual rhythm patterns in the way they type’ (Monrose, 1999). Ecuador bank deployed an Authenware solution to measure online behaviour and keystroke patterns chosen because of its convenience and ability to improve online banking security (PRWEB, 2010). The Bank of Utah also backs this up as they deployed keystroke dynamic technology in a bid to strengthen the scecurity of their internet banking service (Hosseini and Mohammadi 2012). In addition to this, low costs of deployment and minimal changes to the users’ modus operandi may make this technology an attractive investment for banks. |
| Looking beyond technology, there are other factors that affect fraud prevention. Top Management Support has commonly been identified as a CSF for the success of EBanking and is likely to be applicable as a CSF for Fraud Prevention too. This is because to secure e-banking services, a variety of security measures such as encryption (Shah et al, 2012), passwords (Johnson 2007) and One Time Passwords (OTPs) are used. Therefore changes to the modus operandi will be necessary and this wouldn’t be possible without support from the top management. Social and community factors are equally important influencers on the perpetration and prevention of crime (Cecil Eng, 2007). Results from research performed by (Igwe, 2011) agree with this as Socio- Economic factors such as unemployment and poverty both being contributory factors to fraud. Therefore, it is essential that their importance is not underestimated to ensure adequate consideration and emphasis is given. |
| Banking customers’ vulnerability to fraud is another area that has been looked into. (Choplin, 2011) conducted a psychological investigation and found that factors such as education and demographics both had an effect on consumers’ vulnerability. This ties closely to the work of Rizzardi (2008) where emphasis is placed on consumer education to protect their personal information to prevent payment card fraud. Similarly Roberds (1998) reaffirms this by highlighting privacy as a factor that affects the risk of fraud. In addition to this, employees who exploit breakdowns in internal controls commit a large proportion of fraud; strict internal controls have been identified as an effective defence measure for fraud (Sidden, 2005). Similarly, Sidden (2005) reiterated where he states that internal controls are the first and best defence against fraud. This therefore places emphasis on the role that internal audits are required to play to ensure compliance. |
| Given the importance of strict internal controls, it is paramount that not only internal controls exist, but that they are strictly adhered to and policed by internal audits. The importance of internal audits on minimising fraud are highlighted by Coram et al (2008) which concluded that organisations with internal audit functions are more likely to detect and self report fraud than those that don't have internal audit function. In addition to this, the research also found that organisations that have some in-house internal audit function are more effective in detecting and reporting fraud than those that completely outsource the internal audit function. However, it has been argued that internal auditors’ are more costly in comparison to outsourced auditors and that some auditors fear from ‘‘retaliation’’ when reporting fraud related to management and seem less independent (Salameh, 2011). |
| Another likely CSF is organisational learning in the context of fraud vulnerabilities through access to historical lessons learnt. Ganesan (2009) stated, ‘‘the open nature of the Internet, transaction security is likely to emerge as the biggest concern among the ebank’s account holders’’. Signs agreeing with this argument already exist as Roberds (1998) exposes factors from historical lessons learnt where inadequate security measures had led to fraud in retail payment methods. An example was given where cloning that resulted in losses of at least $600 million could beat a store’s value cards encryption. Research by Ganesan (2009) reiterates the importance of protecting customer data via encryption and recommends a hybrid model with a hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem to perform the encryption and decryption processes. |
| An additional security measure that builds on encryption is encouraging the use of agencies that become intermediaries between the customer and banks. Such scenarios help support confidentiality, integrity, and authentication interactions (Tan, 2003) as transactions are not directly linked to the banks systems. |
| The tables below summarise the factors along with their sources and have been categorised into strategic, managerial, operational and technical factors. |
 |
| Managerial Factors |
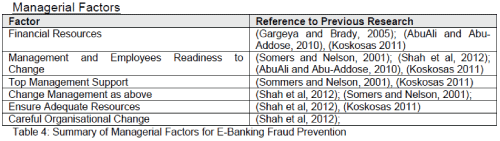 |
| Operational Factors |
 |
| Technical Factors |
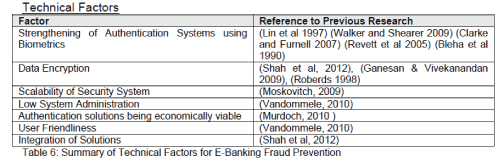 |
| Although there are similarities in factors relating to securing electronic services across industries, inevitably there will also be factors specific to e-banking. Gibson (2011) argued that CSFs for the banking industry are different, particularly in the case of security. Although the review of various literature has exposed factors that could prove critical in improving fraud prevention systems, additional work needs to be done to understand whether the factors are critical to e-banking fraud prevention. |
CONCLUSION |
| Security issues are major barriers to internet banking and e-commerce activities among consumers (Khasawneh, 2009) with fraud highlighted as an important risk associated with payments systems (Roberds, 1998). To secure an e-banking system, IBM placed emphasis on defining clear objectives. This is achieved by understanding the business goals, objectives and critical success factors when planning the security strategy, as well as the impact on the business if they are not achieved (International Business Machines (IBM), 2001). There has been minimal research related to organisations experience on fraud prevention and the critical success factors for e-banking fraud prevention measures. Hence the factors that have been identified require further investigation to understand their criticality. |
| Beyond technology, other effective ways to control security risks need to be administered. This can be achieved by having adaptive policies, procedures and controls (Titrade, 2000). The issue of communication was found to play an important role in ebanking security in addition to organizational flexibility, availability of resources, ebanking project alignment, support from top management, information transparency and security knowledge and awareness (Koskosas, 2011). This compliments results from the work of Akindele (2011) where it was found that lack of adequate training, inadequate communication, and weak leadership styles of supervisors and managers as all causes of fraud. In the UK, online banking has witnessed upto a 32% decline in fraud and this has been attributed to increased customer awareness and fraud detection software in banks (UK Fraud Action, 2010). Therefore indicating that beyond the technological aspects, there is significant impact from customer awareness and exposure to fraud precautionary measures. |
REFERENCES |
Ratiu, C., Craciun., M.D., & Bucerzan, D. (2011). Statistical Model Of The People Confidence In E-Business |
Copyright © 2026 Research and Reviews, All Rights Reserved